- UI (User Interface): Refers to the graphical layout of an application. This includes buttons, text, images, sliders, and all other items the user interacts with. UI design focuses on the look and feel of the product.
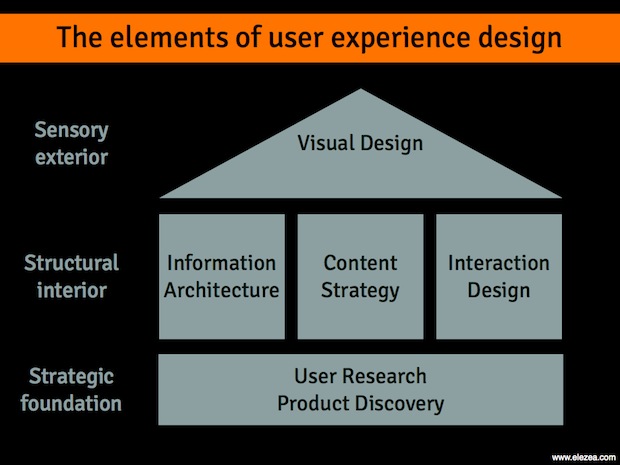
- UX (User Experience): Refers to the user's overall experience with a product. This includes the usability, accessibility, and desirability of the product. UX design focuses on the user's journey to solve a particular problem.